Acorns are not just the fruit of oak trees scattered across autumn forests—they’re nature’s blueprint for understanding the incredible diversity of oak trees. Each acorn offers clues to the species of its parent tree, from the smooth caps of white oaks to the bristly tips of black and red oaks.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the oak tree acorn types, learn how to identify them, and uncover other fascinating facts. So, let’s dig into it!
Main Oak Tree Acorn Types
Oak acorn trees are any tree species that produce acorns, which are the seeds of oak trees. Most oak species start producing acorns around 20 years old, but the peak production occurs between 50 and 80 years, after which acorn production gradually decreases. (Source)
Oak trees hold both ecological and cultural values everywhere. Beyond their ecological importance, oak trees carry immense cultural value. One traditional practice in Armenia is tying cloth pieces to oak tree branches as prayers or wishes for health and prosperity. Oak trees also contribute significantly to the biodiversity of Armenia’s forests, particularly in the Lori and Tavush regions. But we’ll get more on this in detail in the upcoming paragraphs, so stay with us.
To understand the different oak acorn tree types, one should head straight to the extensive library section dedicated to this species. Worry not! I did the legwork for you by breaking down all the information into digestible chunks.
Let’s start with its scientific name, “Quercus”, which is the genus for all oak trees. Under the main genus Quercus, there is a widely known subgenus in the New World clade comprising various sections based on their evolutionary traits. Broadly speaking, the Quercus subgenus has 2 categorized groups:
White Oak (Quercus)
Red Oak (Q. lobatae)
On top of that, black oak, though scientifically grouped in the same section as the red oak, is a distinct and widely appreciated tree species in its own right.
To understand this classification better, let’s have a look at the table below:
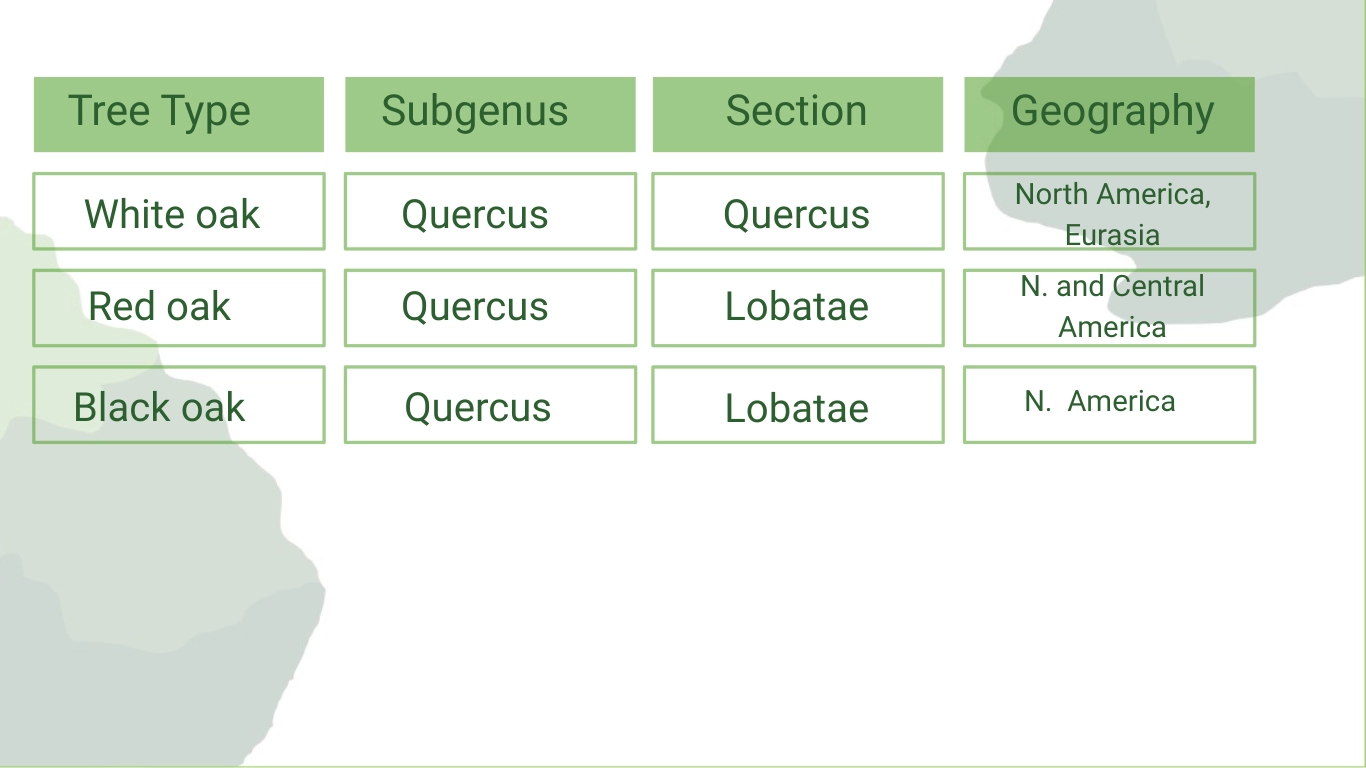
These different tree types, on their own, have numerous species of oak tree acorn maturation and leaf features. Next up, we will go over each group one by one, unveiling more of the oak tree acorns and identifying them.
White Oak Acorn: Species, Identification

Eastern White Oak (Quercus alba)
Quercus alba is characterized by light gray bark with scaly ridges and can grow up to 80 feet tall. The shape of the white oak acorn is oval or slightly oblong, while the cap covers about 25% of the acorn, with a warty texture and a shallow bowl. The color of the Eastern white oak acorn is usually light brown to tan, and it drops from the tree in early fall, typically between September to October.
Bur Oak ( Quercus macrocarpa)
Quercus macrocarpa has deeply lobed leaves with distinctive lobes near the base. Bur oak acorn has an oval or nearly spherical shape and a fringed cap. The cap has a unique “frilly” or “hairy” edge, giving the tree its common name ("bur" oak, from the resemblance to burrs). The color of the burr oak acorn can be light brown to dark brown according to its maturation level.
Caucasian or Persian oak (Quercus macranthera)
Q. macranthera is adapted to high-altitude, cold environments. Leaves are broadly obovate or elliptic, often with deeply lobed or toothed margins. Typical of any white oak acorn, the maturation is in one growing season
Quercus macranthera is native to the Caucasus (Armenia and Georgia) and Western Asia (northern Iran, Turkey). Native trees are nature’s best allies, and that’s why we, at My Forest Armenia, plant only local species in our reforestation and afforestation projects to restore forests, support local wildlife, and biodiversity. Oak is one of the main species of the forests in Armenia. We have planted 343,453 trees and sown 314,772. This represents 29% of all our plantings.
Since its founding, My Forest Armenia has planted over 58,000 Quercus macranthera oak trees, and the numbers continue to increase every year. Find more information about our accomplishments each year in our Annual Reports.Other Species
Sometimes, other oak tree types of subgenus Quercus, section Quercus, are referred to as “white oak group” due to shared characteristics, such as their acorns maturing in a single season and leaves often lacking spiny tips.
One example is Quercus pontica, widely known as Armenian oak, which belongs to the distinct Ponticae section; however, because of shared characteristics of the Quercus section, it might fall under the “white oak” category. Native to Armenia and the Caucasus Mountains, this oak tree type is unfortunately endangered under the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species in 2020.
Red Oak (Quercus Lobatae): Acorns, Identification
Red oak trees are primarily recognized for their reddish-brown wood and stunning red foliage in the fall. Red oak tree acorns mature in two years and have a dark brown or reddish-brown color. Learn here several types of red oak trees and how you can identify them.
Northern Red Oak (Q. rubra):
One of the most well-known red oak species, it is native to eastern and central North America. It is a large deciduous tree that can grow up to 90 feet tall. The leaf shape of Quercus rubra is with deep, sharp lobes. The lobes are pointed with small bristles at the tips. The acorns of Quercus rubra are medium-sized with shallow, saucer-shaped caps covering about a quarter of the acorn.Southern Red Oak (Q. falcata):
Found in the southeastern United States, this oak species grows in a variety of habitats, from upland forests to swamps. It tends to be a smaller tree than the Northern red oak, reaching heights of about 60 to 70 feet. The leaves of the southern red oak have a distinctive shape, often with a falcate (sickle-shaped) appearance.Southern Black Oak (Q. velutina):
Also known as the Eastern Black Oak, this species is native to eastern and central North America. It is important to recognize that black oak trees are not a separate group; they are, in fact, part of the same genus and section as red oaks. The bark of it is dark and deeply furrowed, with a distinct blackish appearance. Black oak tree acorns are medium-sized with a dark, deep brown or black cap that covers about one-third of the nut.
To wrap up
Acorns are more than just seeds: they are nature’s code to unlock the incredible diversity of oak trees. The variety of these trees is remarkable, as each acorn tells a story of geography, adaptation, and ecological significance. So, next time you stroll in the forest or park and spot an oak tree, channel your inner tree detective to identify its acorns and discover where it fits in the oak family. Happy wandering!

